Segment Analysis
Segment Analysis
Market segmentation can be defined as the process of dividing a market into groups or subgroups based on distinct needs, characteristics, or behaviour which might require separate products or marketing mixes. The aim is to match groups of potential customers who have the same set of needs and buyer behaviour. Segmentation encourages businesses to use resources effectively, creates value for the target market, creates focus and effective positioning. However, one of the limitations of marketing segmentation is that targeting multiple segments increases marketing costs.
Requirements for effective segmentation:
- Measurable and identifiable: it must be possible to determine the key variables.
- Accessible: the segments can be reached and served.
- Substantial: the segments should be sufficiently large to be served and profitable.
- Actionable: programs can be developed effectively.
- Unique needs: the segment must respond differently to the market.
Business-to-consumers (B2C) refers to any company primarily focused on selling products and services to consumers. To better understand the behaviours of consumers, market segmentation can be based on:
- Geographical segmentation: city, state, country, climate or density.
- Demographic segmentation: Age, gender, occupation, education, and family life cycle.
- Psychographic segmentation: personality traits, lifestyle or values.
- Behavioural segmentation: usage rate, benefits, attitude towards product or service.
Business-to-business (B2B) refers to any company primarily focused on selling products and services to other business rather than consumers. There are B2B companies in every industry, for example in automobile manufacturing—the manufacturer purchases all materials and components of the vehicle from various suppliers. B2B model requires careful planning and can be segmented by:
- Demographic segmentation: Industry, location or business size.
- Operating variables: customer capabilities, usage status, and technology.
- Purchasing approaches: nature of the relationship, purchasing criteria and policies.
- Situational factors: specific application, order size, urgency.
- Personal characteristics: benefits, attitude towards the product or service.
Using Segment Analysis on Planium Pro
To complete this section, on the left-hand side menu bar, click the + to expand the ‘Marketing’ menu and select ‘Segment Analysis’
Step 1: Segmentation
The segmentation process begins by identifying all potential segments that the market can be broken into. This is followed by diving further into creating sub-segments if applicable. Lastly, each segment will have different elements that have to be identified and described.
This process will provide a step-by-step guide to segment the market. Add one segment at a time. All the segments identified will be listed below.
Click ‘Next’ to start the segmentation process.
Step 2: Add a new Segment
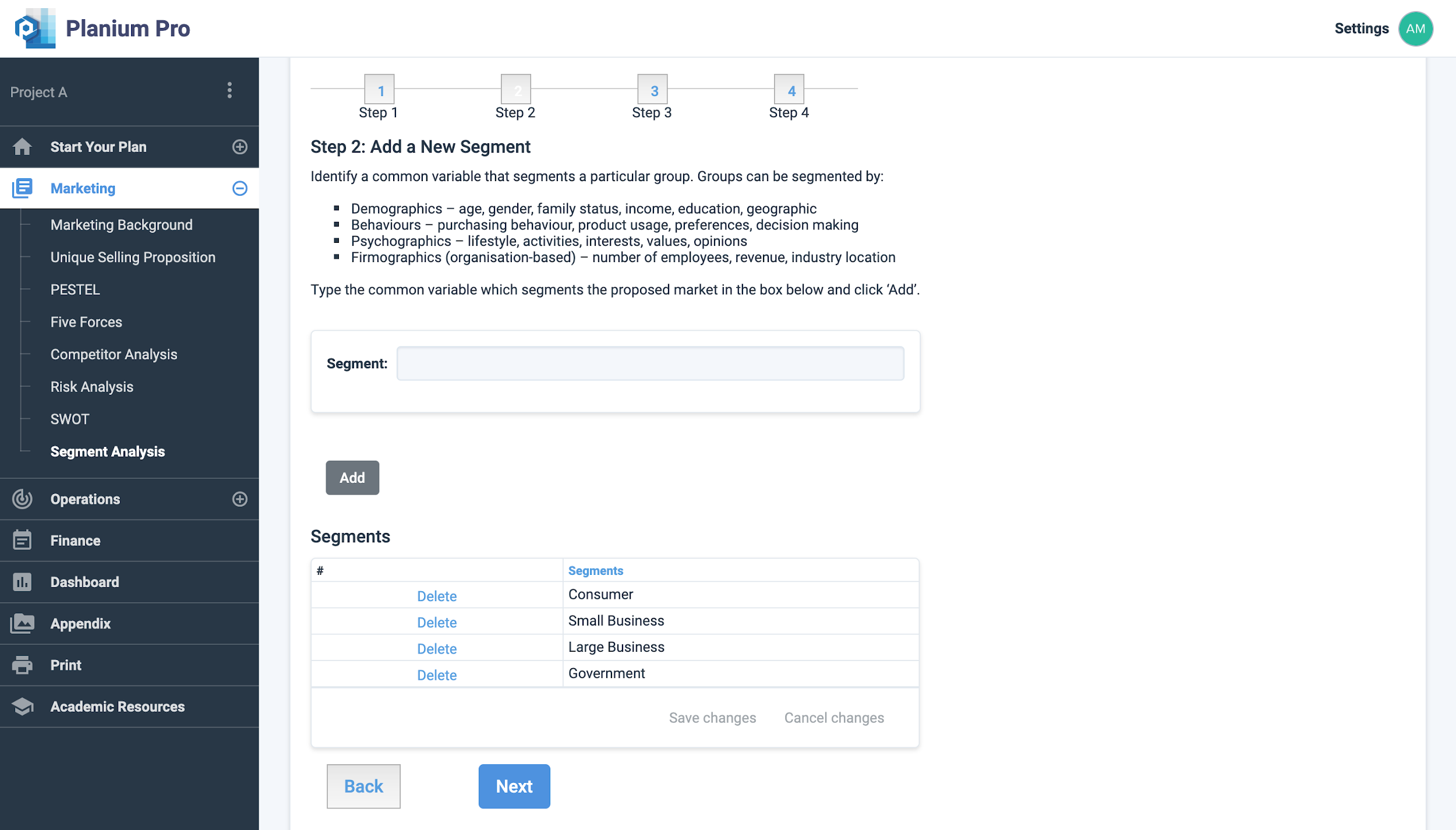
Choose a common variable for your market segmentation:
- Demographics – age, gender, family status, income, occupation.
- Behaviour – Purchasing behaviour, product usage, preferences, decision making.
- Psychographics – lifestyle, activities, interests, opinions.
- Firmographics (organisation-based)- number of employees, revenue, industry location.
Type the common variable which segments the proposed market in the box below and click ‘Add’. Add as many segments the business may have.
Click ‘Next’ to move to the next step in the segmentation process.
Step 3: Segment Structure
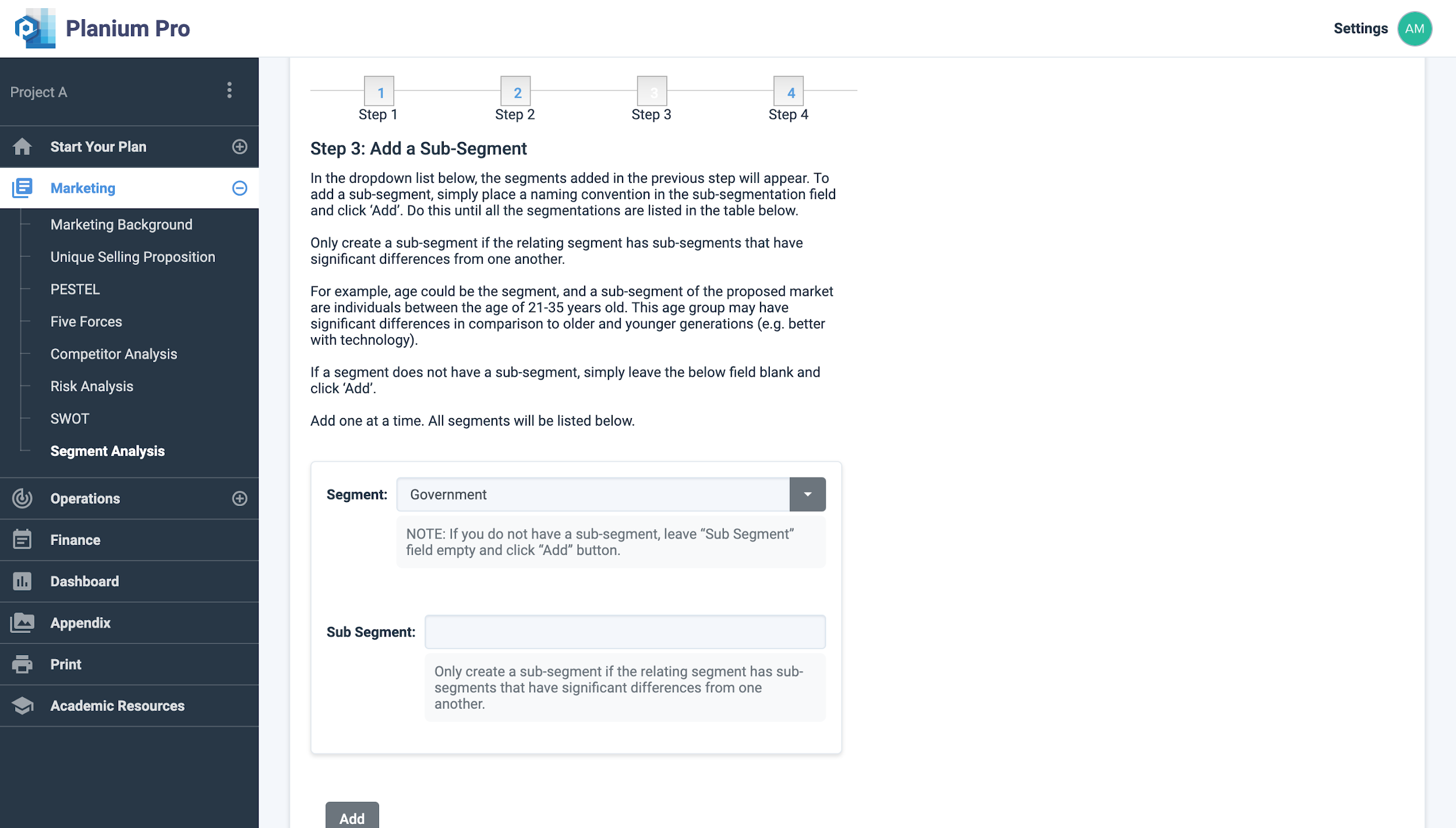
- Segment: If there is sub-segment, then leave this field empty and click ‘Add’
- Sub Segment: only create a sub-segment if the relating segment has sub-segment that have significant difference from one another.
Click ‘Next’ to move to the next step in the segmentation process.
Step 4: Segmentation Details
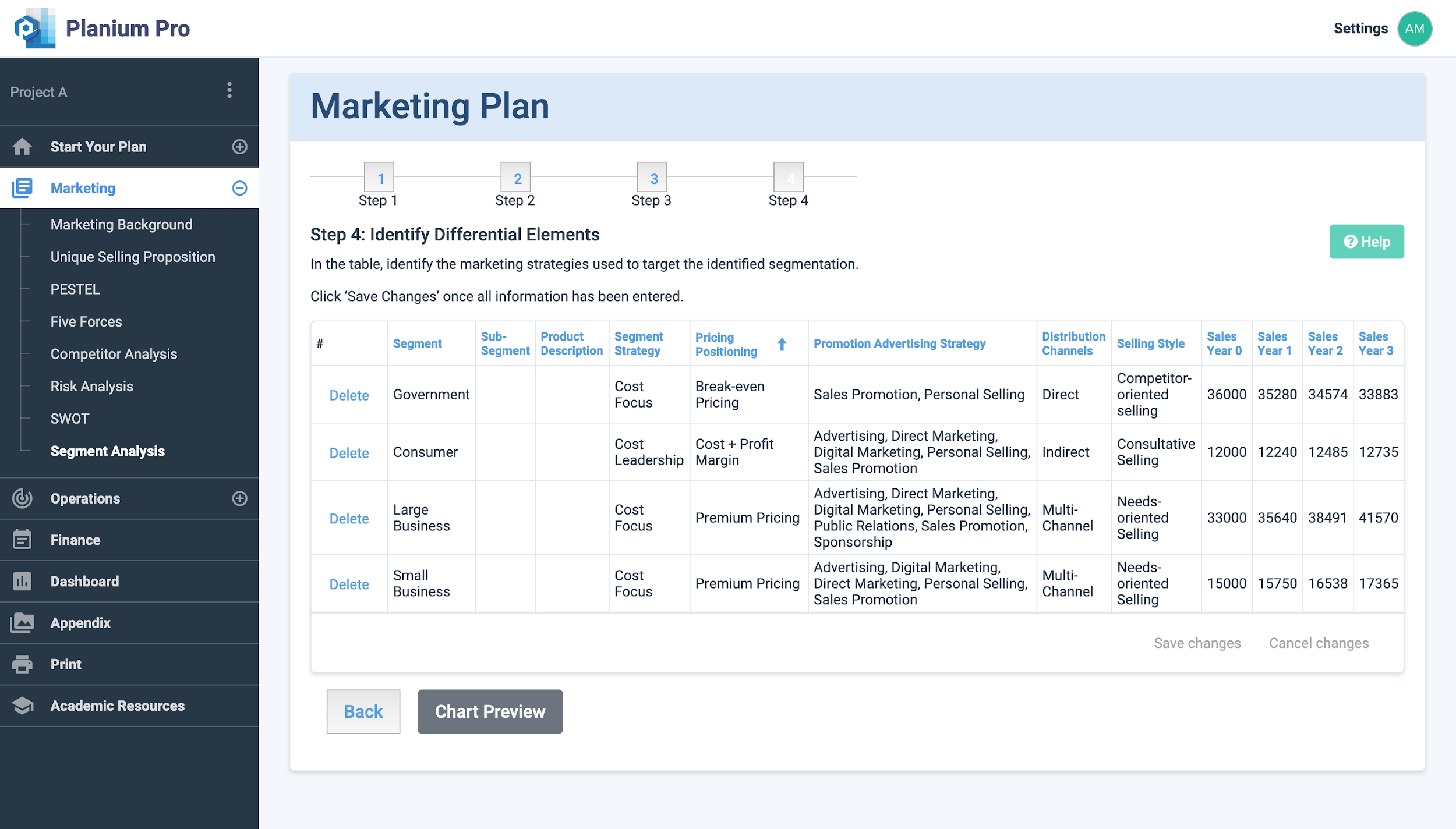
This final stage produces a summary table where you can identify the type of pricing positioning, marketing strategy and distribution channels should be used in each segment.
Descriptors for each of the fields are listed below:
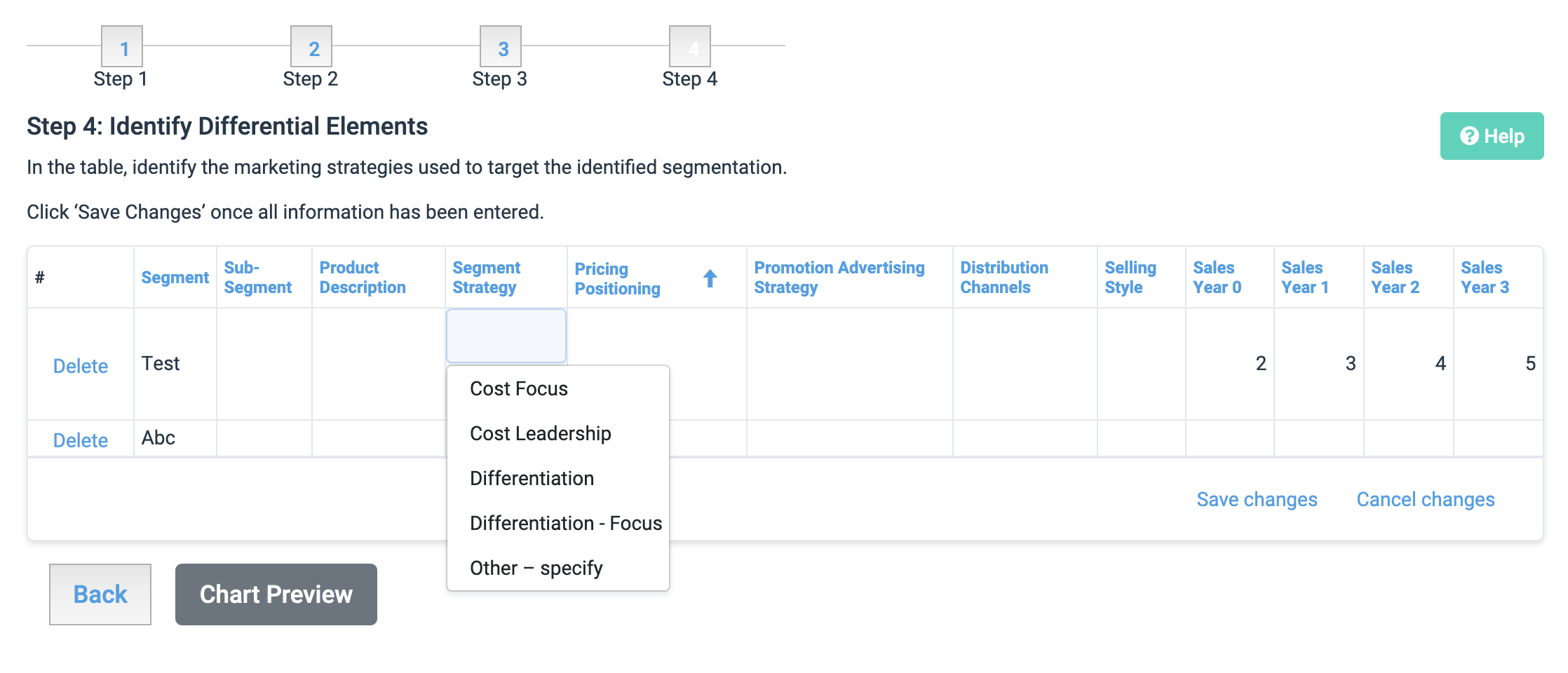
Segment Strategy:
Cost Leadership: no frills approach to minimise cost for the business
Cost Focus: emphasising cost-minimisation within a focused market
Differentiation: creating uniquely desirable products and services
Differentiation Focus: pursuing strategic differentiation within a focused market
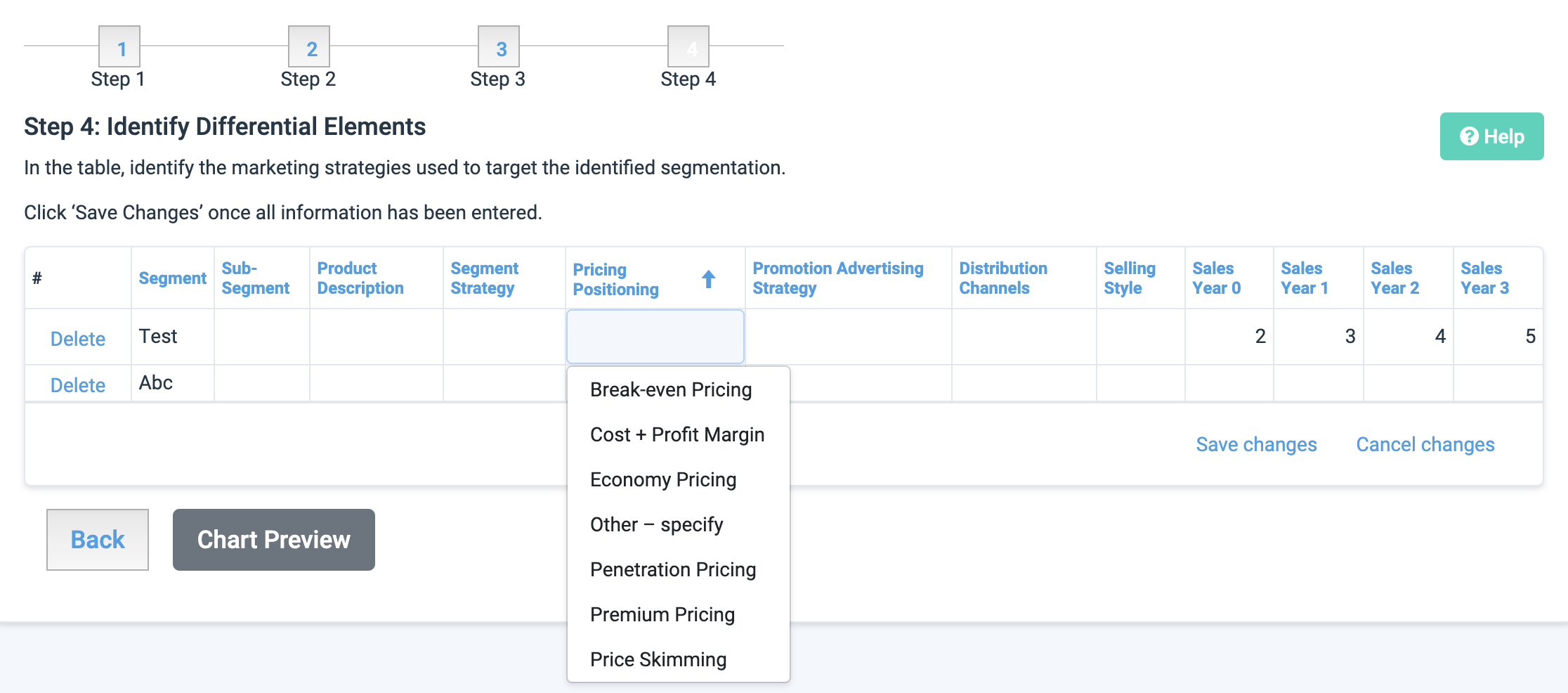
Pricing Positioning:
Break-even Pricing: revenue is equal to cost
Cost + Profit Margin: revenue is more than cost, resulting in a profit margin
Economy Pricing: low marketing and production costs, suited to large sales volumes
Penetration Pricing: low prices on goods and services to attract buyers, initial loss of income
Premium Pricing: costs higher than competitors, often used for unique goods
Price Skimming: high introductory prices, lowering slowly with new competitors
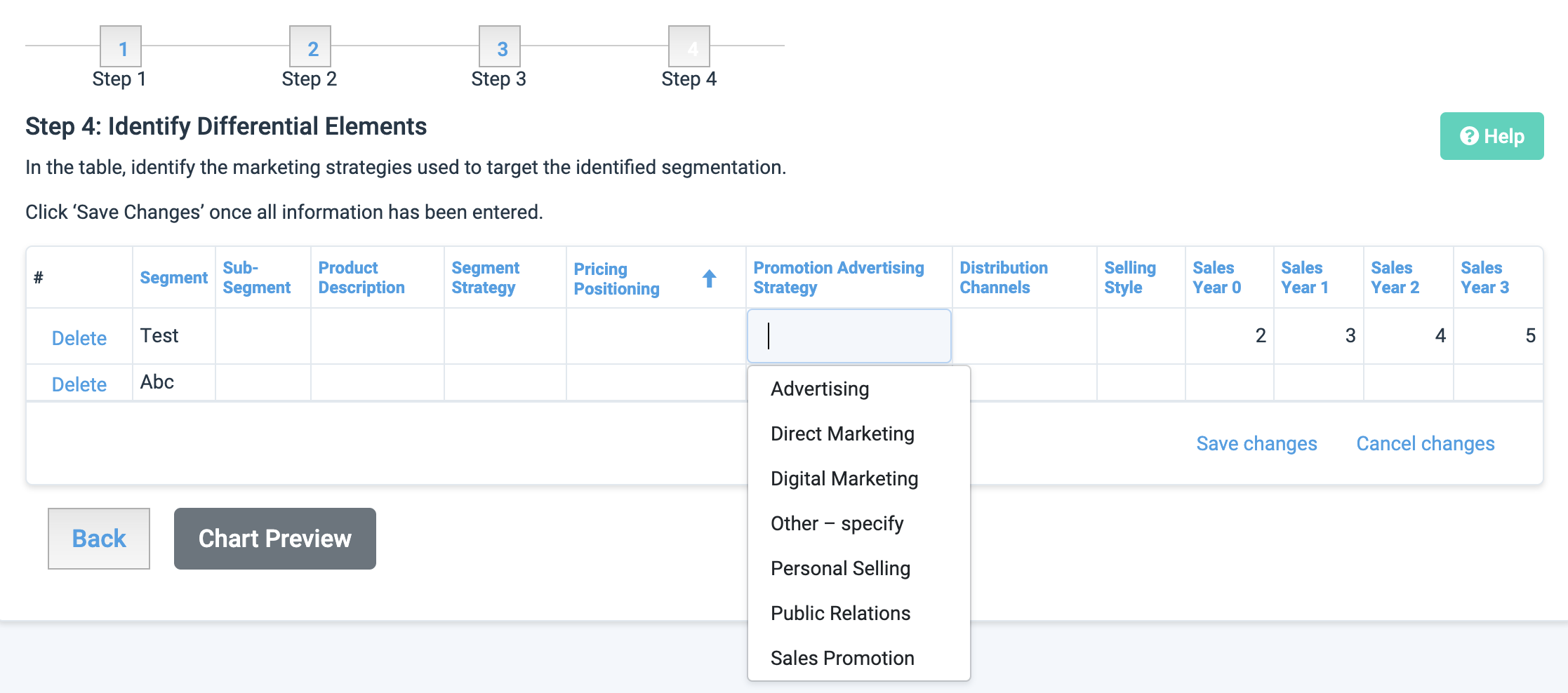
Promotion Advertising Strategy:
Advertising: advertisements (radio, tv, billboard, newspaper, magazine), infomercials
Direct Marketing: point-of-sale displays, telemarketing, email
Digital Marketing: website, social media, blogging, newsletter sign-up
Personal Selling: utilising personal networks and connections
Public Relations: media introductions, PR events, news/media releases
Sales Promotion: coupons, discounts, referral programs, loyalty incentives

Distribution Channels:
Direct: direct to end-user without any interference
Indirect: involves third-parties such as wholesalers, retailers, licensing, franchisee
Multi-channel: utilising multiple channels simultaneously to reach end-user
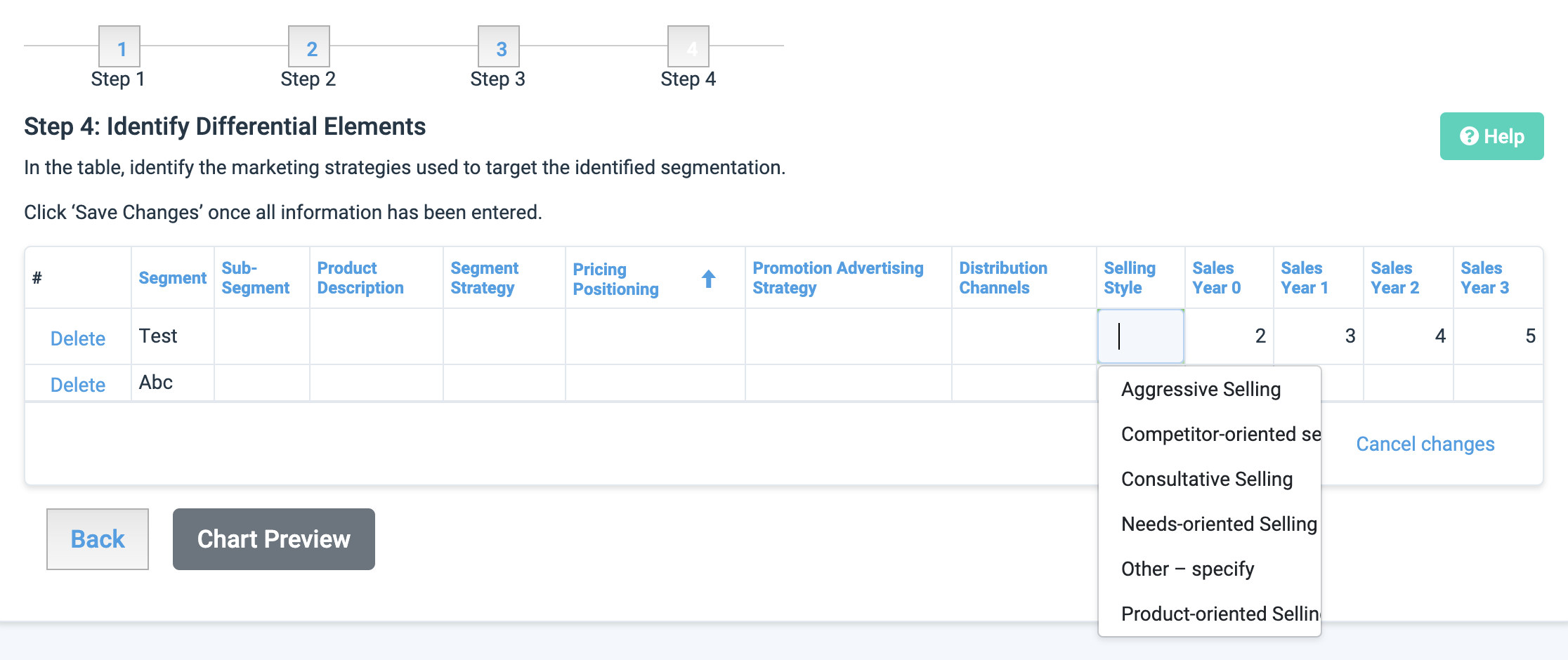
Selling Style:
Aggressive Selling: hard-driving selling style, highly focused on making sales on first attempt
Competitor-Oriented Selling: overcomes buyer objections by highlighting benefits over competitors
Consultative Selling: aims to get the best possible result for the buyer, sale occurs over time
Needs-Oriented Selling: focus is on buyer needs, ability to be highly tactful and a problem-solver
Product-Oriented Selling: explain features and benefits until buyer is convinced of benefits
Once all fields have been filled, enter the predicted sales for the first 3 years of the business.
Click ‘Save’ to save changes.
Click ‘Chart Preview’ to view the analysis results.
Analysing Segment Analysis Results on Planium Pro
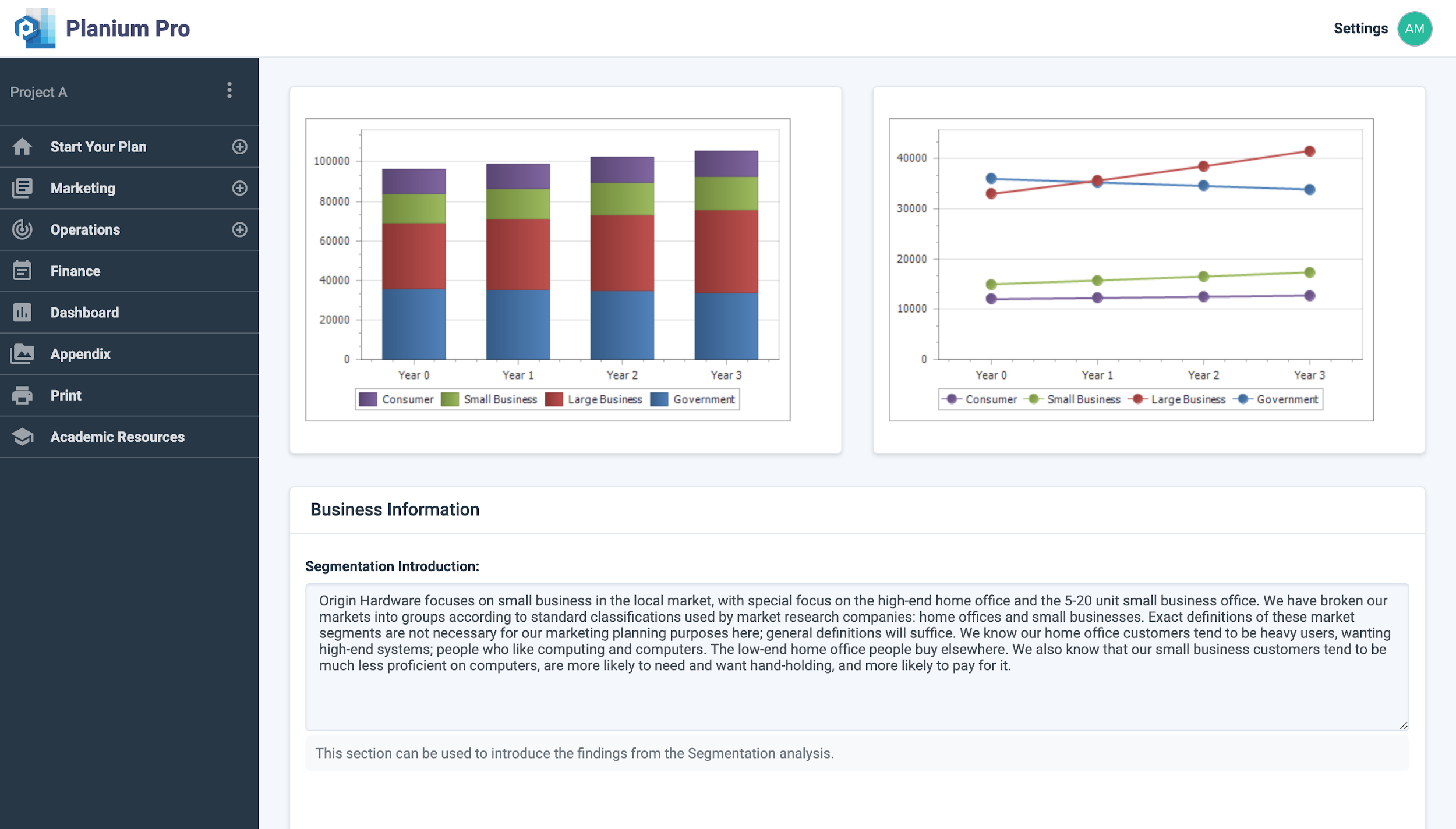
Under ‘Segment Analysis Introduction’, you can input any introductory information that may benefit your client or investor.
‘Analysis Results’ is the section to write-up the analysis on the graph and describe any key themes that are present in the data.
Click ‘Save’ to save changes.
Click ‘Report Preview’ to view the write-up in report format.







